Data Pipeline Orchestration, Management, and Monitoring: Tools, Steps, and Best Practices
How orchestration, management, and monitoring ensure smooth, efficient, and reliable data pipelines. Learn best practices, modern tools, and key performance metrics that help organizations optimize data flow, enhance reliability, and maintain real-time visibility across complex analytics environments.

Introduction
In the era of data-driven enterprises, orchestration, management, and monitoring form the foundation of a reliable data pipeline infrastructure. These elements ensure that data flows efficiently, accurately, and securely from sources to destinations, supporting analytics, AI models, and business intelligence systems.
Orchestration focuses on coordinating and automating data pipeline tasks, ensuring dependencies are managed and that ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) workflows execute in the correct order.
Management involves optimizing pipeline resources, scheduling, error handling, and maintaining resilience against failures.
Monitoring provides real-time visibility into pipeline health, enabling teams to detect performance issues, data delays, or integrity failures before they impact decision-making.
Together, these three pillars ensure data integrity, scalability, and operational reliability across modern cloud and hybrid environments; from AWS Data Pipeline and Azure Data Factory to Apache Airflow and Prefect.
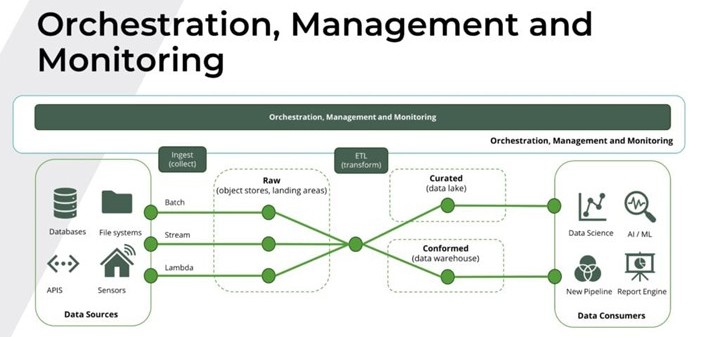
1. Orchestration in Data Pipelines
What is Orchestration?
Orchestration in data pipelines refers to the automated coordination and sequencing of ETL processes, ensuring that data moves seamlessly from raw input to refined output. Modern orchestration tools like Apache Airflow, Dagster, and Google Cloud Composer help automate workflows, manage task dependencies, and reduce manual intervention.
Why Orchestration is Necessary
Orchestration is essential for maintaining data consistency and process efficiency across complex pipelines. It eliminates manual scheduling, improves resource utilization, and ensures the automation of repetitive data operations.
Key reasons orchestration is vital include:
- Task Coordination: Ensures ETL steps run in the right order and that downstream processes receive accurate inputs.
- Dependency Management: Guarantees that dependent tasks execute only after prerequisites are complete.
- Error Handling and Recovery: Enables automated retries, error alerts, and rollbacks to protect data integrity.
- Scalability: Supports distributed processing across multiple nodes or cloud clusters to handle growing data volumes.
How Orchestration Can Be Organized
- Workflow Design: Define dependencies and execution flow using code-based DAGs (Directed Acyclic Graphs) or visual interfaces.
- Task Scheduling: Implement time-based or event-driven triggers using cron jobs or API events.
- Resource Allocation: Dynamically assign compute resources to optimize cost and performance.
- Monitoring and Logging: Use Airflow logs, Prometheus, or Grafana dashboards to track workflow success and detect bottlenecks.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Orchestration
- Task Success Rate – Measures pipeline reliability and automation stability.
- Task Latency – Evaluates workflow efficiency and identifies bottlenecks.
- Error Rate – Tracks the frequency of task failures.
- Resource Utilization – Monitors compute, memory, and storage efficiency.
- Time to Recovery – Measures resilience and fault tolerance after errors.
Effective orchestration enhances automation, scalability, and system resilience — transforming raw data flows into dependable, production-grade pipelines.
2. Management in Data Pipelines
What is Data Pipeline Management?
Management in data pipelines involves governing the processes, configurations, and resources that enable seamless data movement. It focuses on pipeline versioning, scheduling, scaling, and governance, ensuring high performance and operational stability.
Why Management is Necessary
Proper management ensures that pipelines are efficient, resilient, and cost-effective. It provides structure for error handling, enables rapid issue resolution, and supports version control for pipeline reproducibility.
Key benefits of pipeline management include:
- Resource Optimization: Prevents over-provisioning and improves cost efficiency.
- Error Handling and Resilience: Enhances fault tolerance with automated rollback mechanisms.
- Scheduling and Automation: Reduces manual tasks with CI/CD integration and timed executions.
- Version Control: Tracks pipeline updates and configurations via Git-based repositories.
- Scalability: Enables horizontal and vertical scaling to manage growing data volumes and workloads.
How to Organize Pipeline Management
- Resource Scheduling: Use Kubernetes or Apache Mesos to manage workloads efficiently.
- Error Handling Systems: Implement alerting and retry logic to minimize downtime.
- Version Control: Leverage Git for tracking code and configuration updates.
- Configuration Management: Apply Ansible or Terraform for automated deployments.
- Centralized Monitoring: Use ELK Stack or CloudWatch for log aggregation and insight visualization.
Key KPIs for Data Pipeline Management
- Pipeline Uptime: Reflects system reliability and operational stability.
- Task Completion Time: Measures process efficiency.
- Error Rate: Indicates robustness of pipeline operations.
- Change Failure Rate: Tracks deployment or update stability.
- Incident Response Time: Evaluates support efficiency and responsiveness.
Strong pipeline management empowers organizations to maintain consistent performance, lower operational costs, and enhance governance.
3. Monitoring in Data Pipelines
What is Data Pipeline Monitoring?
Monitoring ensures the continuous visibility, measurement, and optimization of data pipeline health, performance, and reliability. It’s essential for maintaining data accuracy and ensuring compliance with service level agreements (SLAs).
Why Monitoring is Necessary
Without continuous monitoring, pipelines can suffer from silent failures, latency spikes, or data drift, impacting analytics and AI outcomes. Monitoring enables teams to detect, diagnose, and resolve issues in real time, ensuring uninterrupted data flow.
Core benefits include:
- Real-Time Issue Detection: Identifies errors and performance drops early.
- Data Quality Assurance: Monitors for data loss, duplication, or corruption.
- Performance Optimization: Tracks throughput and latency for tuning.
- Compliance and Auditing: Ensures traceability for data governance frameworks.
- Resource Management: Balances workloads for cost and performance optimization.
How Monitoring Can Be Organized
- Define KPIs: Identify success metrics (e.g., throughput, latency, uptime, error rate).
- Implement Tools: Adopt Prometheus, Datadog, ELK Stack, or CloudWatch for real-time tracking.
- Set Up Alerts: Configure alerts for anomalies and threshold breaches.
- Visualize Data: Build Grafana or Kibana dashboards for performance insights.
- Automate Responses: Automate scaling, recovery, or restarts based on alert triggers.
Key KPIs for Monitoring
- Pipeline Throughput – Data processed per second/minute.
- Task Success Rate – Percentage of successfully executed jobs.
- Error Rate – Frequency of processing or connection failures.
- System Uptime – Availability and operational reliability.
- Alert Response Time – Speed of incident detection and resolution.
- Data Quality Metrics – Accuracy, completeness, and consistency of datasets.
Proactive monitoring not only prevents data disruptions but also provides actionable intelligence for continuous performance improvement.
Want to Learn More? Become a Certified Enterprise Big Data Engineer
The DASCIN Enterprise Big Data Engineer (EBDE®) certification is ideal for professionals involved in designing and maintaining Big Data infrastructure and pipelines. It provides comprehensive insights into Big Data architecture, orchestration, storage, and processing mechanisms essential for enterprise-scale analytics.
Knowledge - Certification - Community




